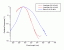
Repair:
- in progress: Photorepair
of Cyclobutane Pyrimidine Dimers in Sorghum
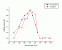 Action Spectrum
Action Spectrum
Info:
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Action Spectra of DNA Photolyases for Photorepair of Cyclobutane Pyrimidine Dimers in Sorghum and Cucumber, Megumi Hada ,Yoko Iida and Yuichi Takeuchi, Plant Cell Physiol. 41(5): 644–648 (2000) [03.057]
Source: Dig. from Ref.
- in progress: Photorepair
of Cyclobutane Pyrimidine Dimers in Cucumber
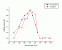 Action Spectrum
Action Spectrum
Info:
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Action Spectra of DNA Photolyases for Photorepair of Cyclobutane Pyrimidine Dimers in Sorghum and Cucumber, Megumi Hada ,Yoko Iida and Yuichi Takeuchi, Plant Cell Physiol. 41(5): 644–648 (2000)[03.057]
Source: Dig. from Ref.
- in progress: Photoreactivation
of UV-induced inhibition of pluteus-formation in sea
urchin eggs
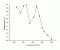 Action Spectrum
Action Spectrum
Info:
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: EJIMA Y.,IKENAGA M.,SHIROYA T, ACTION SPECTRUM FOR PHOTOREACTIVATION OF ULTRAVIOLET-INDUCED MORPHOLOGICAL ABNORMALITY IN SEA URCHIN EGGS, PHOTOCHEMISTRY AND PHOTOBIOLOGY :40 (1984): 461-464[03.058]
Source:
Phototoxic Reactions:
- Phototoxic reactions
induced by anthracene (Immed. Erythema, Delayed Erythema, Weals
and Flares)
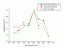 Action Spectrum
Action Spectrum
Info:
Altitude factor: 1.xx-1.xx
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: K.H. Kaidbey, S.Nonaka PP39(3) 375-378, 1984[03.059]
Source:
Internal: actionspectra, teil_7.op.
Human General Risk:
- ACGIH 1990
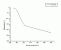 ACGIH action spectrum
ACGIH action spectrum  Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)
 RAF (O3, sh)
RAF (O3, sh)
Info:
Altitude factor: 1.09-1.20
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: ACGIH, 1990: Treshold limit values and biological exposure indices for 1990-1991. American Conference of Industrial Hygienists, Cincinnati, Ohio, USA.
Source: Madronich priv.com. UVMod
- ACGIH 1971
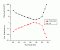 ACGIH action spectrum
+Thresholds
ACGIH action spectrum
+Thresholds
Info: This action spectrum was gained as convolution of Photokeratitis (Rabbit and Primates[03.00xx] ) and Erythema ( [03.0xx ....]
Altitude factor: 1.xx-1.xx
Treshold Dose HT: see Action spectrum
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Sliney D.H., The Merits of an envelope action spectrum for Ultraviolet Radiation Exposure Criteria, AmericanIndustrial Hygiene Association Journal:33 :644-653 (1972)
Source: Table from Ref. [03.005][UVLIT 332]
Internal: Actionspectra_5_normen.xls, wirkungsf_teil_acgih.opj,
Skin Cancer:
Skin cancer associated with exposure to UV are the basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and curaneous melanoma. The first two result from the malignant transformation of keratinocytes. The later results from malignant transformation of melanocyten (pigment producing cells).
- under
re-arrangement: SCUP
Action Spectrum
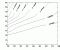 Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3) RAF (O3,
sh)
RAF (O3,
sh)
Info:
Altitude factor: 1.09-1.19
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: de Gruijl, F.R. and J.C. van der Leun, 1994: Estimate of the wavelength dependency of ultraviolet carcinogenesis in humans and its relevance to the risk assessment of a stratospheric ozone depletion. Health Phys., vol 67, 319-325.[03.020]
Source: UVMod
Internal: actionspectra, teil_x.op.
- SCUP-H
Action spectrum
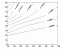 Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)  RAF (O3,sh)
RAF (O3,sh)
Info:
Altitude factor: 1.09-1.17
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
de Gruijl, F.R. and J.C. van der Leun, 1994: Estimate of the wavelength dependency of ultraviolet carcinogenesis in humans and its relevance to the risk assessment of a stratospheric ozone depletion. Health Phys., vol 67, 319-325.[03.020]
Source: F.R. de Gruijl, private comm.
- Photocarciogenesis
(Non-Melanoma skin cancer
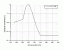 Action Spectrum
Action Spectrum
Info: This action specterum is identical with SCUP-H
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: CIE TC6-32 report, 2000
Source: Ref. [03.004]
- Photocarciogenesis
(skin edema)
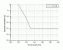 Action Spectrum
Action Spectrum
Info: The authors showed that the A.S for mouse edema (48h after exposure) is appropriate to describe photocarciogenesis. Kelfkens et al. extended the A.S. by staying constant from 330nm to 400nm.
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: C.A. Cole, D. Forbes, R.E. Davies, An action spectrum for UV photocarcinogenesis, Photochem. Photobiol. 43 (1986) 275–284.[03.017]
Source: G. Kelfkens, F.E. de Gruijl, J.C. van der Leun, Ozone depletion and increase in annual carcinogenic ultraviolet dose, Photochem. Photobiol. 52 (1990) 819–823 [03.008].
Internal: actionspectra, teil_x.op.
- missing: Photocarciogenesis
(skin edema)
Action Spectrum
Info: The authors showed that the A.S for mouse edema (24h after exposure)
Ref.: C.A. Cole, R.E. Davies, D. Forbes, D'Aloisio, xxxxxxxx, Photochem. Photobiol. 37 (1983) 623-631.
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Source: Digit. from: H. Slaper, J.C. van der Leun, (1987), Human exposure to ultraviolet radiation: quantitative modelling of skin cancer incidence, In: Human exposure to ultraviolet radiation: Risks and regulations (edited by W.F. Passchier and B.F.M.Bosnjakovic, Excerpta Medica International Congress Series 744, Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. 155-171.[03.011]
Internal: actionspectra, teil_x.op.
- Photocarciogenesis
(based on STSL)
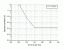 Action Spectrum
Action Spectrum
Info: Action spectrum of Sternborg and van der Leun (see below) modified by Slaper (1987) in the UVA.
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: G. Kelfkens, F.E. de Gruijl, J.C. van der Leun, Ozone depletion and increase in annual carcinogenic ultraviolet dose, Photochem. Photobiol. 52 (1990) 819–823.[03.008]
Source: Digit. from Ref.
Internal: actionspectra, teil_x.op.
- Photocarciogenesis
(based on PTR)
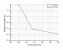 Action Spectrum
Action Spectrum
Info: The authors showed that the A.S for mouse edema (48h after exposure) is appropriate to describe photocarciogenesis. Kelfkens et al. extended the A.S. by staying constant from 330nm to 400nm.
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: ????G. Kelfkens, F.E. de Gruijl, J.C. van der Leun, Ozone depletion and increase in annual carcinogenic ultraviolet dose, Photochem. Photobiol. 52 (1990) 819–823. [03.008]
Source: Digit. from Ref. ????
Internal: actionspectra, teil_x.op.
- Photocarciogenesis -
Tumorgenesis
Action Spectrum
Info: IT is derived from numerous experiments on albino heirless mice. It bases on the UV dose needed to induce tumors in 50% of the exposed mice.Tthis is a very direct approximation of an action spectrum for UV-carciogenesis.
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Sterenborg H.J.C.M, J.C. van der Leun, Action spectra for tumorigenesis by ultraviolet radiation, in: Human expusore to ultrabviolet radiation risks and regulations (eds. W.F.Passchier and B.F.M. Bosnjakovic), Excerpta Medica 744,173-190, Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987.[03.032]
Source: Ref.
Internal: actionspectra, teil_x.op.
Pigmentation:
Pigmentation is strategy to counteract high radiation levels. Immediant pigmentation results from oxydative mealnin darkening, which is reversible. It occurs after receiving a threshold dose and vanishes depending on the received days after minutes or days. After receiving a certain threshold dose, melanin pigments are built up and spread. Delayed pigmentation vanishes after weeks.
- under
reconstruction: Direct (immediant)
Pigmentation
Action spectrum
 Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)  RAF (O3,sh)
RAF (O3,sh)
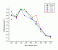 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Info: This sction apectrum was averaged by the authors over Skin Type 3, 4 and 5.
Altitude factor: 1.08-1.09
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation: xxx Loc.: --- Vol.: Human
Ref.: Ch. Irwin, A. Barnes, D. Veres, K. Kaidbey,An ultraviolet radiation action spetrum for immediate Pigment darkening, Photochem.Photobiol. 57, 504-507[03.053]
Source: Digit. in Ref.
- in progress: Direct
(immediant) Pigmentation ST3
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Info: This sction apectrum was derived for Skin Type 3.
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation: xxx Loc.: --- Vol.: Human
Ref.: Ch. Irwin, A. Barnes, D. Veres, K. Kaidbey,An ultraviolet radiation action spetrum for immediate Pigment darkening, Photochem.Photobiol. 57, 504-507[03.053]
Source: Digit. from Ref.
- in progress: Direct
(immediant) Pigmentation ST4
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Info: This sction apectrum was derived for Skin Type 4.
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation: xxx Loc.: --- Vol.: Human
Ref.: Ch. Irwin, A. Barnes, D. Veres, K. Kaidbey,An ultraviolet radiation action spetrum for immediate Pigment darkening, Photochem.Photobiol. 57, 504-507[03.053]
Source: Digit. from Ref.
- in progress: Direct
(immediant) Pigmentation ST5
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Info: This sction apectrum was derived for Skin Type 5.
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation: xxx Loc.: --- Vol.: Human
Ref.: Ch. Irwin, A. Barnes, D. Veres, K. Kaidbey,An ultraviolet radiation action spetrum for immediate Pigment darkening, Photochem.Photobiol. 57, 504-507[03.053]
Source: Digit. from Ref.
- Delayed (persistent)
Pigmentation ST 1+2
Action spectrum
 Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)  RAF (O3,sh)
RAF (O3,sh)
Info: Delayed pigmentation for individuas with low pigmentation potential.
Altitude factor: 1.09-1.18
Thresold Dose: 1MTD =450 J/m2
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: CIE, Reference Action spectra for ultraviolet induced erythema and pigmentation of Different human skin types, in: Technical Collection 1993/3 p.15-21, 1993
Source: Ref. [03.003]
Internal: actionspectra, teil_x.op.
- Delayed (persistent)
Pigmentation ST 3+4
Action spectrum
 Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)
 RAF (O3,sh)
RAF (O3,sh)
Info: Delayed pigmentation for individuas with medium pigmentation potential.
Altitude factor: 1.08-1.17
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Thresold Dose: 1MTD =450 J/m2
Ref.: CIE, Reference Action spectra for ultraviolet induced erythema and pigmentation of Different human skin types, in: Technical Collection 1993/3 p.15-21, 1993
Source: Ref. [03.003]
Internal: actionspectra, teil_x.op.
Immune suppression
The UVB activated
photoreceptor urocanic acid regulates immune suppression in mice.
The same compound exists on other mammalian skin, including human
skin.
- Immune suppresion
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Info: in vivo action spectrum for systematic immune suppression in the BALB/c mouse adapted by extrapolation from: E.C. de Fabo, F.P. Noonan, Mechanism of immune suppressionby ultraviolet irradiation in vivo. I. Evidence for the existance of a unique photoreceptor in skin and its role in photoimmunologym J.Exp.Med. 158, 94-89, 1983..
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation: ???chromatic Loc.: in vivo Vol.: BALB/c mouse
Ref.: E.C. de Fabo, F.P. Noonan, J.Frederick, Biologically effective doses of sunligth for immune supression at various latitudes and their relationship to changes in stratospheric ozone, Photochem. Photobiol. Vol.52, No. 4, 811-817, 1990 [03.016]
Source: Digit. from Ref.
Internal: actionspectra, teil_x.op.
- Trans to cis
Photoisomerisation of urocanic acid in vitro
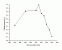 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Info: .
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation: ???chromatic Loc.: in vivo Vol.: xxx
Ref.: N.K. Gibbs,M. Norval, N.J. Traynor, M. Wolf, B.E. Johnson, J. Crosby, Action spectra for the trans to cis photoisomerisation of urocancic acid in vitro and in mouse skin, Photochem.Photobiol., 57(3), 584-590, 1993 [03.077]
Source: Digit. from Ref.
- Trans to cis
Photoisomerisation of urocanic acid in mouse skin
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Info:
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation: ???chromatic Loc.: xxxx Vol.: mouse skin
Ref.: N.K. Gibbs,M. Norval, N.J. Traynor, M. Wolf, B.E. Johnson, J. Crosby, Action spectra for the trans to cis photoisomerisation of urocancic acid in vitro and in mouse skin, Photochem.Photobiol., 57(3), 584-590, 1993 [03.077]
Source: Digit. from Ref.
- Production of
cis-Urocanic acid in vitro from trans-Urocanic acid
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Info:
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation: monochromatic Loc.: in vitro Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Jones et al. [03.108]
Source: Digit. from Ref.
Vitamin D3:
Vitamin D is formed in the skin after exposure to ultraviolet radiation (and is also absorbed from diet). It is hydroxylated at the liver to 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D), and again in the kidney to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25(OH)2D), which is the active form (Schemata). Effective dose is assumed to be less than 1MED.
- Vitamin D3
 Action Spectrum
Action Spectrum  Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)
 RAF (O3,sh)
RAF (O3,sh)
Info:
Altitude factor: 1.11-1.17
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: MacLaughlin JA, Anderson RR, Holick MF. Spectral character of sunlight modulates the photosynthesis of previtamin D3 and its photoisomers in human skin. Science. 1982; 1001-1003.
Source: M.F. Holick, private comm.siehe auch Madronich priv.com.
Internal: actionspectra, teil_x.op.
Enzyms
- Aldolase
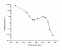 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Info:
Altitude factor: x.xx-x.xx
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: R.B. Setlow +
Source: Digit. from Richard B. Setlow, Reflections in Mutation Research: Shedding light on proteins, nucleic acids, cells, humans and fish, Mutation Research 511 (2002) 1-14 [03.038]
Internal: Actionspectra.xls wirkugsf_teil8.opj
- TRYPSIN
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Info:
Altitude factor: x.xx-x.xx
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: R.B. Setlow +
Source: Digit. from Richard B. Setlow, Reflections in Mutation Research: Shedding light on proteins, nucleic acids, cells, humans and fish, Mutation Research 511 (2002) 1-14[03.038]
Internal: Actionspectra.xls wirkugsf_teil8.opj
Phototherapy:
- in progress: Psoriasis
Action spetcrum
Ebiol(sh,O3)
RAF(O3,sh)
Info: Psoriasis is a very common dermatological indication for phototherapy. The UV radiation "hemmt" the increase "Teilungsrate" of basal cells in the upper skin.
Ref.: DIN 5031-10, 2000. [03.007]
Source: Ref.
Mammals:
- SCUP-M
Action Spectrum
 Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3) RAF (O3,sh)
RAF (O3,sh)
Info: SCUP in mice
Altitude factor: 1.09-1.18
Ref.: Ref. see SCUP
Source: see SCUP
- Mammalian cell
mutagenicity
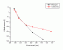 Action Spectrum
Action Spectrum
Info: Average of several action spectra
Altitude factor:
Ref.: R.B. Setlow, E. Grist, K. Thompson, A.D. Woodhead (1993) Wavelengths effective in induction of malignant melanoma, Proc. Natl.Acad. Sci. USA, Vol. 90, 6666-6670.
Source: Digit. from Ref.
- Mammalian cell
cytotoxicity
 Action Spectrum
Action Spectrum
Info: Average of several action spectra
Altitude factor: x.xx-x.xx
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: R.B. Setlow, E. Grist, K. Thompson, A.D. Woodhead (1993) Wavelengths effective in induction of malignant melanoma, Proc. Natl.Acad. Sci. USA, Vol. 90, 6666-6670.
Source: Digit. from Ref.
- Damage to lens of pig eyes
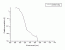 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Info:
Altitude factor: x.xx-x.xx
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Oriowo, M. et al. (2001). Action spectrum for in vitro UV-
induced cataract using whole lenses. Invest. Ophthalmol. &
Vis. Sci. 42, 2596-2602.
Source: S. Madronich priv. comm
- in progress: Rabbit Cornea
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Info:
Altitude factor: x.xx-x.xx
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Pitts D.G., Cullen A.P., Hacker P.D. (1977), Ocular effects of ultraviolet radiation from 295 to 365nm, Invest. Opthal.Vis.Sci. 16(10): 932-939.
Source: Digit. from D.H. Sliney (1987),Unintentional exposure to ultraviolet radiation: risk reduction and exposure limits, In: Human exposure to ultraviolet radiation: Risks and regulations (edited by W.F. Passchier and B.F.M.Bosnjakovic, Excerpta Medica International Congress Series 744, Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. 425-437.[03.012]
Internal: Actionspectra_4_eyes.xls wirkugsf_teilx.opj
- in progress:
Erythema Rabbit
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Info:
Altitude factor: x.xx-x.xx
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Freeman
Source: xxx. from Ref. [03.048]
Internal: Actionspectra_7_ery.xls wirkugsf_teil_ery.opj
- in progress:
Hyperplasmia in hairless mice
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Info:
Altitude factor: x.xx-x.xx
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Sterneborg + van der Leun
Source: xxx. from Ref. [03.037]
Internal: Actionspectra.xls wirkugsf_teil_skin.opj
Plankton:
- Phytoplankton
(Antarctic) photoinhibition
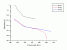 Action spectrum
Action spectrum  Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)
 RAF (O3,sh)
RAF (O3,sh)
Info:
Altitude factor: 1.09-1.16
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Mitchell, B.G., "Action Spectra for ultraviolet photoinhibition of Antarctic phytoplankton and a model of spectral diffuse attenuation coefficients", In Response of Marine Phytoplankton to Natural Variations in UV-B Flux, (Edited by G. Mitchell, I. Sobolev and O. Holm-Hansen), Proc. of Workshop, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla, CA, April 5, 1990
Source: ????
Internal: xxxx.xls wirkugsf_teil_xxxx.opj
- Phytoplankton
(Antarctic) photoinhibition
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Info: In original paper, value of b and m are given as positive.
Correct values are negative. Also, limit to positive
values.
Altitude factor: x.xx-x.xx
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Boucher, N., Prezelin, B.B., Evens, T., Jovine, R., Kroon, B., Moline, M.A., and Schofield, O., Icecolors '93: Biological weighting function for the ultraviolet inhibition of carbon fixation in a natural antarctic phytoplankton community, Antarctic Journal, Review 1994,
pp. 272-275, 1994.
Source:
Internal: xxxx.xls wirkugsf_teil_xxxx.opj
- Phytoplankton
photoinhibition (Prorocentrum micans)
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum  Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)  RAF (O3,sh)
RAF (O3,sh)
Info:
Altitude factor: 1.09-1.13
Altitude factor: x.xx-x.xx
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Cullen, J. J., P. J. Neale and M. P. Lesser, 1992: Biological weighting function for the inhibition of phytoplankton photosynthesis by ultraviolet radiation. Science. 258, 646-650.
Source:
- Phytoplankton
photoinhibition (Phaeodactylum sp.)
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum  Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)  RAF (O3,sh)
RAF (O3,sh)
Info:
Altitude factor: 1.08-1.12
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Cullen, J. J., P. J. Neale and M. P. Lesser, 1992: Biological weighting function for the inhibition of phytoplankton photosynthesis by ultraviolet radiation. Science. 258, 646-650.
Source:
Internal: xxx_.xls wirkugsf_teil_xxxx.opj
- Zooplankton mortility
(Boeckella gracilipes)
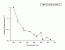 Action
spectrum
Action
spectrum
Info:
Altitude factor: x.xx-x.xx
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation: natrual solar Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: Boeckella gracilipes
Ref.: B. Tartarotti, W. Cravero, H.E. Zagarese, (2000) Biological weighting function for the mortality of Boeckella gracilipes (Copepoda, Crustacea) derived from experiments with...Photochem Photobiol, 72(3), 314-319 [03.079]
Source: Dig. from Ref.
Internal: actionspectra_2_aquatic.xls wirkugsf_teil_aquatic.opj
- Buma et al.
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum
Wirkungsf_teil8.opj
MAA:
Mycrosporint-like amino acids
(MAA) are photoprotective compounds. Cynobakteria, Phytoplankton,
Macroalgea or Seagras produce MAA as strategy of phtoprotection.
- MAA Sinha
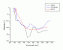 Action spectrum
Action spectrum Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)  RAF (O3,sh)
RAF (O3,sh)
Info:
Altitude factor: 1.08-1.13
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Sinha 1990 [03.061]
Source: D.P.Häder
Internal: xxxx.xls wirkugsf_teil_xxxx.opj
- MAA Klisch
 Action
spectrum
Action
spectrum Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)  RAF (O3,sh)
RAF (O3,sh)
Info:
Altitude factor: 1.09-1.11
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Klisch + Häder [03.060]
Source: D.P.Häder
Internal: xxxx.xls wirkugsf_teil_xxxx.opj
- MAA Gröninger
(Phaeodactylum sp.)
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)
 RAF (O3,sh)
RAF (O3,sh)
Info:
Altitude factor: 1.09-1.14
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation:xxx Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: xxx
Ref.: Gröninger + Häder [03.073]
Source: D.P.Häder
Internal: xxxx.xls wirkugsf_teil_xxxx.opj
Aquatic:
- Cod egg mortality
 Action spectrum
Action spectrum Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)
 RAF (O3,sh)
RAF (O3,sh)
Info:
Altitude factor: 1.09-1.14
Ref.: Kouwenberg et al., 1999, Marine Biology
Source:
- Calanus Finmarchicus
mortality action spectrum
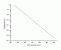 Action spectrum
Action spectrum Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)
 RAF (O3,sh)
RAF (O3,sh)
Info:
Altitude factor: 1.09-1.14
Ref.: Kouwenberg et al., 1999, Marine Biology
Source:
Fish:
- Melanoma Induction in
Platyfish-swordtail Hybrids
Action spectrum
 Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)
 RAF (O3,sh)
RAF (O3,sh)
Info:
Altitude factor: 1.09-1.10
Ref.: Setlow, R.B., E. Grist, K. Thompson, and A.D. Woodhead. 1993. Wavelengths effective in induction of malignant melanoma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U.S.A., 90: 6666-6670. [03.0xx]
Source: R.B. Setlow, private comm.
Action Spectra in the UVA and Visual range
Vitals:
- Photo-Synthese
Action spectrum
 Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)
Info: The effectiveness starts at 385nm
Altitude factor: 1.07
Ref.: DIN5031-10 1979 (replaced in 2000) [03.006]
Source: Ref.
- Chlorophyl-Synthese
Action spectrum
 Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)
Info: The effectiveness starts at 385nm
Altitude factor: 1.07
Ref.: DIN5031-10, 1979 (replaced by change in 2000) [03.006]
Source: Ref.
Phototropism:
- Photo-Tropism in
Plants
Action Spectrum
 Ebiol(sh,O3)
Ebiol(sh,O3)
Info:The effectiveness starts at 385nm
Altitude factor: 1.07
Ref.: DIN5031-10 1979 (replaced in 2002) [03.006]
Source: Ref.
- Photo-Tropism in
Phycomyces (Chen)
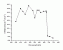 Action
spectrum
Action
spectrum
Info:
Altitude factor: x.xx-x.xx
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation: monochrom. Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: Phycomyces blakesleeanus (wild type) strain NRRL1555
Ref.: Action spectrum for subliminal light control of adaptation in Phycomyces phototropism. Chen X.Y., Xiong Y.Q., Lipson E.D., Photochem-Photobiol. 1993 Sep; 58(3): 425-31[03.098]
Source: Tabled in Ref.
Internal: actionspectra_10_phototropismc.xls wirkugsf_teil_phototropism.opj
- Photo-Tropism in
Phycomyces (Galand)
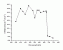 Action
spectrum
Action
spectrum
Info:
Altitude factor: x.xx-x.xx
Treshold Dose HT:
Radiation: monochrom. Loc.: xxxxxx Vol.: ---
Ref.:Galand P., Orejas M., Lipson E.D. (1989) Light-controlled adaption kinetics in Phycomyces: evidence for a novel yellow-light absorbing pigment, PP 49, 493-499
Source: Dig. from [03.098]
Internal: actionspectra_10_phototropismc.xls wirkugsf_teil_phototropism.opj
Phototaxis:
Light plays also a major role in orientation of
non-photosynthetic organisms which use ligth as a directional cue
to move. Movements are done also to avoid high irradiance or to
avoid radiation of harmful wavelengths. It is thougth that in
many ciliated protozoa photo-orientation additionally serves
nutritional needs or to avoid predators.
- Negative phototactic
reaction in Chlamydodon mnemosyne
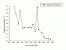 Action Spectrum
Action Spectrum
Info: Chlamydodon mnemosyne is a cryptophorid ciliate, feeds on cynobacteria. It is thougth that blue ligth receptor molecules e.g. flavins of flavin-likepoigments are responsible forligth perception and trigger phototactic orientation. Negative phototactic reaction denotes movement away from the ligth source.
Ref.:Selbach M., Häder D.-P., Kuhlmann H.-W., Phototaxis in Chlamydodon mnemosyne:determination of the illuminance-response curve and the action spectrum, J.of Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol. 49, 35-40, 1999. [03.062]
Source: Digit. from Ref.
- schematic:
Phototactic orientation of flagelates: Gymnodinium,
Chlamydomonas, Cryptomonas, Cosmarium, Porphyridium
Info:.
Ref.:
Source:
- schematic:
Phototaxis, Photokinese and Photophobie of Phormidium
uncinatum
Info:.
Ref.:
Source:
- shematic:
Phototropismus in Phycomyces,Absorption Riboflavin,
Absorption of beta-karotin in hexan
Info:.
Ref.:
Source:
- Schematic: Absorption
spectra of variuos molecules
Info:.
Ref.:
Source:
- Schematic: Absorption
spectra of important biological substances
Info:.
Ref.:
Source:
- Schematic: Action
spectrum for different kinds of phase shifts
Info:.
Ref.:
Source:
- Schematic: Action
spectrum for inhibition of length grow
Info:.
Ref.:
Source:
- Bilirubin
Dissoziation
Info:
Ref.: DIN5031-10, 1979, changed in 2000
Source: Ref.
Spectral Sensitivity of broadband meter
- Eldonet UVA
Info:
Ref.:
Source:.
- Eldonet PAR
Info:
Ref.:
Source:.
Wanted:
- Skin:
Melanogenesis 17
Skin cancer in SKH-1 hairless mice (Utrecht) : F.R. de Gruijl, J.J.C.M. Sterenborg, P.D. Forbes, R.E. Davies, C. Cole, G. Kelfkens, H. van Weelden, H. Slaper, J.C. van der Leun, Wavelength dependence of skin cancer induction by ultraviolet irradiation of albino hairless mice, Cancer Res. 53 (1993) 53–60.
- DNA-related:
Mutagenicity and fibroblast killing, in: F. Zolzer, J. Kiefer, Wavelength dependence of inactivation and ¨ mutation induction to 6-thioguanine-resistance in V79 Chinese hamster fibroblasts, Photochem. Photobiol. 40 (1984) 9–53.
Mutagenicity and fibroblast killing, in: M.J. Peak, J.G. Peak, M.P. Moehring, R.B. Webb, Ultraviolet action spectra for DNA dimer induction, lethality, and mutagenesis in Escherichia coli with emphasis on the UVB region, Photochem. Photobiol. 40 (1984) 613–620.
Fibroblast killing, in: S.M. Keyse, S.H. Moses, D.J.G. Davies, Action spectra for inactivation of normal and xeroderma pigmentosum human skin fibroblasts by ultraviolet radiation, Photochem. Photobiol. 37 (1983) 307–312.
Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer formation, in: G.L. Chan, M.J. Peak, J.G. Peak, W.A. Haseltine, Action spectrum for the formation of endonuclease-sensitive sites and (6–4) photoproducts induced in a DNA fragment by ultraviolet radiation, Int. J. Radiation Biol. 50 (1986) 641–648.
(6-4) photoproduct formation in: G.L. Chan, M.J. Peak, J.G. Peak, W.A. Haseltine, Action spectrum for the formation of endonuclease-sensitive sites and (6–4) photoproducts induced in a DNA fragment by ultraviolet radiation, Int. J. Radiation Biol. 50 (1986) 641–648.
HIV-1: in B. Stein, H.J. Rahmsdorf, A. Steffen, M. Litfin, P. Herrlich, UVinducedDNAdamage is an intermediate step in UV-induced expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, collagenase, c-fos, and metallothionein, Mol. Cell. Biol. 9 (1989) 5169–5181. - Eyes:
Damage of coronea in [32] D.G. Pitts, A.P. Cullen, P.D. Hacker, Ocular effects of ultraviolet radiation from 295 to 365 nm, Invest. Ophthalmol. 16 (1977) 932– 939.
Damage to lens (cataract) in [32] - Other effects on
animal cells:
Occupational exposure limit, in ACGIH (American Conference of Governmental and Industrial Hygienists), 1991–1992 Threshold Limit Values, 1992.
Immune supression, in E.C. DeFabo, F.P. Noonan, Mechanism of immune suppression by ultraviolet radiation in vivo. I. Evidence for the existence of a unique photoreceptor in skin and its role in photoimmunology, J. Exp. Medicine 158 (1983) 84–98.
Cell mortality in Chinese hamster, [35] H. Banrud, K. Berg, T. Platou, J. Moan, An action spectrum for UV-induced attachment of V79 Chinese hamster cells to a substratum, Int. J. Radiation Biol. 64 (1993) 437–444. - Membrane Damage:
Membrane-bound K+ -stimulated ATPase inactivation in C.W. Imbrie, T.M. Murphy, UV-action spectr
um (254–405 nm) for inhibition of a Kq-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase from a plasma membrane of Rosa damascena, Photochem. Photobiol. 36 (1982) 537–542. - Plants:
Isoflavonoid formation in bean, E. Wellmann, UV-B-Signal/Response-Beziehungen unter natur- ¨ lichen und artifiziellen Lichtbedingungen, Ber. Deutsch. Bot. Ges. 98 (1985) 99–104.
Photosynthetic electron transport, L.W. Jones, B. Kok, Photoinhibition of chloroplast reactions, I. Kinetic and action spectra, Plant Physiol. 41 (1966) 1037–1043.
Overall photosynthesis in leaf of Rumex patentia,R.D. Rundel, Action spectra and the estimation of biologically effective UV radiation, J. Invest. Opthalmol. 58 (1983) 360–366.
DNA-damage in Alfalfa F.E. Quaite, B.M. Sutherland, J.C. Sutherland, Action spectrum for DNA damage in alfalfa lowers predicted impact of ozone depletion, Nature 358 (1992) 576–578. - Phytoplankton:
Inhibition of motiliy (Euglena gracilis),D.-P. Hader, R.C. Worrest, Effects of enhanced solar ultraviolet ¨ radiation on aquatic ecosystems, Photochem. Photobiol. 53 (1991) 717–725.
Inhibition of photosynthesis,J.J. Cullen, P.J. Neale, M.P. Lesser, Biological weighting function for the inhibition of phytoplankton photosynthesis by ultraviolet radiation, Science 258 (1992) 646–649.
in Antarctic community,N.P. Boucher, B.B. Prezelin, Biological weighting functions for the ´ UV inhibition of carbon fixation in a natural Antarctic phytoplankton community, Marine Ecol. Progress Ser. 144 (1996) 233–236.
Inhibition of photosynthesis (Nodularia spumigena, cyanobacterium),D.-P. Hader, R.C. Worrest, H.D. Kumar, R.C. Smith, Effects of ¨ increased solar UV-B irradiation on aquatic ecosystems, in: J.C. van der Leun, M. Tevini (Eds.), Environmental Effects of Stratospheric Ozone Depletion—1994 Update, United Nations Environmental Programme, Nairobi, Kenya, 1994. - Tropospheric photolysis: all Ref.45 O3 q h n ª O( 1 D) q O2 U, O3 q h n ª O( 3 P) q O2, H2 O2 q h n ª OH q OH 0, HNO3 q h n ª OH q NO2, NO2 q h n ª O( 3 P) q NO, HCHO q h n ª H q CHO, HCHO q h n ª H2 q CO, W.P. de More, S.P. Sander, D.M. Golden, R.F. Hamspon, M.J. Kurylo, C.J. Howard, A.R. Ravishankara, C.E. Kolb, M.J. Molina, Chemical kinetics and photochemical data for use in stratospheric modeling, Evaluation Number 12, JPL Publication 97-4, Pasadena, CA, 1997.
- Aquaeous
photochemistry:
CO production (Suwannee River), R. Valentine, R.G. Zepp, Formation of carbon monoxide from photodegradation of terrestrial organic matter, Environ. Sci. Technol. 27 (1993) 409–412.
CO production (Pacific Ocean), 47O.C. Zafirou, personal communication, 1998.
COS production (Gulf of Mexico), 48 R.G. Zepp, M.O. Andreae, Factors affecting the photochemical formation of carbonyl sulfide in seawater, Geophys. Res. Lett. 21 (1994) 2813–2816.
COS production (North Sea), 48
Photodegradation of nitrate ions,R.G. Zepp, J. Hoign, H. Bader, Nitrate-induced photooxidation of trace organic chemicals in water, Environ. Sci. Technol. 21 (1987) 443–450.
Photodegradation of HCHO (Biscayne Bay),R.J. Kieber, X. Zhou, K. Moper, Formation of carbonyl compounds from UV-induced photodegradation of humic substances in natural waters: fate of riverine carbon in the sea, Limnol. Oceanogr. 35 (1990) 1503–1515.
Photoproduction of H2O2 in freshwater W.J. Cooper, R.C. Zika, R.G. Patasna, J.M. Plane, Photochemical formation of hydrogen peroxide in natural waters, Environ. Sci. Technol. 22 (1988) 1156–1160. - Materials
damage Yellowness induction in polyvinyl chloride,52 A.L. Andrady, A. Torikai, K. Fueki, Photodegradation of rigid PVC formulations. III. Wavelength sensitivity to light-induced yellowing by monochromatic light, J. Appl. Polymer Sci. 37 (1989) 935–946.
Yellowness induction in polycarbonate [53] A.L. Andrady, K. Fueki, A. Torikai, Spectral sensitivity of polycarbonates to light-induced yellowing, J. Appl. Polymer Sci. 42 (1991) 2105–2107.
References:
A,B,C:
D,E,F:
Diffey B L and Farr P M 1988 The action spectrum in drug induced
photosensitivity Photochem. Photobiol. 47 49-54
Errera M 1952 Etude photochemique de l'acide désoxyribonucleique
I. Mesures énergétiques Biochim. Biophys. Acta 8 30-7
G,H,I,J:
Gates F L 1928 On nuclear derivatives and the lethal action of
ultraviolet light Science 68 478-80
Harm W 1980 Biological Effects of Ultraviolet Radiation (Cambridge:
Cambridge University Press)
Jagger J 1985 Solar-UV Actions on Living Cells (New York:
Praeger) pp 174-6
K,L,M:
N,O,P,Q:
Patrick M H and Rahn R O 1976 Photochemistry of DNA and
polynucleotides: photoproducts Photochemistry and Photobiology
of Nucleic Acids vol II ed S Y Wang (New York: Academic) pp
35-95
R,S,T:
U,V,W:
X,Y,Z:
Last modification: July, 2003 alois.schmalwieser()vetmeduni.ac.at